![]() This panel is English as default and cannot be localized to other languages.
This panel is English as default and cannot be localized to other languages.
Trimble GPS Settings panel - General tab
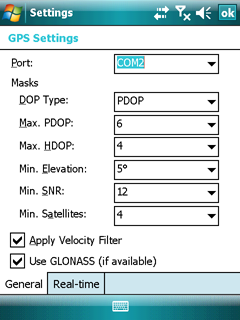
Port: Displays the available GPS serial ports. Select a COM port here before connecting to the GPS receiver. If you specify the wrong port, your application cannot communicate with the GPS receiver. The default port setting is COM1.
Masks
DOP Type: Default: PDOP. Use this property to specify whether to use a maximum PDOP or a maximum HDOP value to control whether the GPS receiver is computing positions. A low DOP value indicates that the visible satellites are widely separated in the sky, which gives better position information. When the DOP value rises above the maximum setting, the application stops logging positions.
![]() When using a Juno SB, Juno SC, or Juno ST handheld, a GPS Pathfinder XB receiver, or a GPS Pathfinder XC receiver, or the Trimble Yuma rugged tablet computer, Trimble recommends that you set the DOP type to PDOP and then set the MaximumPDOPMask property to 99
When using a Juno SB, Juno SC, or Juno ST handheld, a GPS Pathfinder XB receiver, or a GPS Pathfinder XC receiver, or the Trimble Yuma rugged tablet computer, Trimble recommends that you set the DOP type to PDOP and then set the MaximumPDOPMask property to 99
Max. PDOP: Default: 6.0. Use this property to view and set the maximum Position Dilution of Precision (PDOP) for the satellite constellation. If the Trimble GPS receiver detects a higher PDOP value for the current satellite constellation, the receiver stops computing positions until the PDOP drops to or below the value of this property.
The PDOP value indicates the quality of a GPS position. It takes account of the location of each satellite relative to the other satellites in the constellation, and their geometry in relation to the GPS receiver.
Specify a lower maximum PDOP to collect fewer, more precise positions. However, decreasing the maximum PDOP too far below the value recommended for your GPS receiver significantly decreases the time during which you can calculate positions, and does not significantly increase accuracy.
Specify a higher maximum PDOP to collect more, less precise positions. However, increasing the maximum PDOP can seriously degrade position quality.
Legal values for this property are 1-99. A PDOP value of 4 or less gives excellent positions. A PDOP of between 4 and 8 is acceptable. A PDOP of 8.0 or more is poor. The default maximum PDOP is 6.
![]() When using a Juno SB, Juno SC, or Juno ST handheld, a GPS Pathfinder XB receiver, or a GPS Pathfinder XC receiver, or the Trimble Yuma rugged tablet computer, set the maximum PDOP to 99.
When using a Juno SB, Juno SC, or Juno ST handheld, a GPS Pathfinder XB receiver, or a GPS Pathfinder XC receiver, or the Trimble Yuma rugged tablet computer, set the maximum PDOP to 99.
Max. HDOP: Default: 4.0. Use this property to view and set the maximum Horizontal Dilution of Precision (HDOP) for the satellite constellation. If the Trimble GPS receiver detects a higher HDOP value for the current satellite constellation, the receiver stops computing positions until the HDOP drops to or below the value of this property.
![]() When using a Juno SB, Juno SC, or Juno ST handheld, a GPS Pathfinder XB receiver, or a GPS Pathfinder XC receiver, or the Trimble Yuma rugged tablet computer, Trimble recommends that you do not use this property. Instead, set the DOP Type property to PDOP and then set the Max. PDOP property to 99.
When using a Juno SB, Juno SC, or Juno ST handheld, a GPS Pathfinder XB receiver, or a GPS Pathfinder XC receiver, or the Trimble Yuma rugged tablet computer, Trimble recommends that you do not use this property. Instead, set the DOP Type property to PDOP and then set the Max. PDOP property to 99.
Specifying a maximum HDOP can give greater productivity than filtering the solutions with a maximum PDOP. Setting a maximum PDOP rejects some positions that have an acceptable HDOP value, because their VDOP (Vertical Dilution of Precision) value is unacceptable. When you use a maximum HDOP, these positions are accepted.
Use the HDOP setting when vertical precision is not particularly important, and your position yield would be decreased by excluding positions with a high vertical component in the PDOP value (for example, if collecting data under canopy).
Legal values for this property are 1-99. The maximum HDOP should typically be set to approximately two-thirds of your normal PDOP setting. An HDOP value of 4 or less gives excellent positions.
Min. Elevation: Default 15°. Use this property to view and set the maximum Position Dilution of Precision (PDOP) for the satellite constellation. If the Trimble GPS receiver detects a higher PDOP value for the current satellite constellation, the receiver stops computing positions until the PDOP drops to or below the value of this property.
The PDOP value indicates the quality of a GPS position. It takes account of the location of each satellite relative to the other satellites in the constellation, and their geometry in relation to the GPS receiver.
Specify a lower maximum PDOP to collect fewer, more precise positions. However, decreasing the maximum PDOP too far below the value recommended for your GPS receiver significantly decreases the time during which you can calculate positions, and does not significantly increase accuracy.
Specify a higher maximum PDOP to collect more, less precise positions. However, increasing the maximum PDOP can seriously degrade position quality.
Legal values for this property are 1-99. A PDOP value of 4 or less gives excellent positions. A PDOP of between 4 and 8 is acceptable. A PDOP of 8.0 or more is poor. The default maximum PDOP is 6.
![]() When using a Juno SB, Juno SC, or Juno ST handheld, a GPS Pathfinder XB receiver, or a GPS Pathfinder XC receiver, or the Trimble Yuma rugged tablet computer, set the maximum PDOP to 99.
When using a Juno SB, Juno SC, or Juno ST handheld, a GPS Pathfinder XB receiver, or a GPS Pathfinder XC receiver, or the Trimble Yuma rugged tablet computer, set the maximum PDOP to 99.
Min. SNR: Default: 39. Use this property to view and set the minimum signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) value of each satellite tracked by the Trimble GPS receiver. The SNR is a measure of the quality of the signal from a satellite. When the SNR of a satellite falls below the minimum value, the receiver stops using that satellite to calculate GPS positions.
![]() If you lower the minimum SNR, the GPS receiver uses satellites with weaker signals. While this may increase the GPS coverage you can obtain in environments where the GPS signal is weakened (such as forests), it can reduce accuracy.
If you lower the minimum SNR, the GPS receiver uses satellites with weaker signals. While this may increase the GPS coverage you can obtain in environments where the GPS signal is weakened (such as forests), it can reduce accuracy.
Applications created using version 2.00 and later of the GPS Pathfinder Tools SDK store and display SNR values as Carrier-to-Noise ratio (C/No) values, measured in decibel-Hertz (dBHz). Applications created using previous versions of the SDK stored and displayed signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) values as Amplitude Measurement Unit (AMU) values.
The typical SNR of a satellite at 30° elevation is between 47 and 50 dBHz. The quality of a GPS position degrades as the SNR of one or more satellites in the constellation falls below 39 dBHz.
Legal values for the Minimum SNR property range from 12 to 47 dBHz. Typical Minimum SNR Mask values for most supported Trimble GPS receivers are 33 to 43 dBHz.
![]() When using a Juno SB, Juno SC, or Juno ST handheld, a GPS Pathfinder XB receiver, or a GPS Pathfinder XC receiver, or the Trimble Yuma rugged tablet computer, Trimble recommends that you set the minimum SNR to 12 dBHz.
When using a Juno SB, Juno SC, or Juno ST handheld, a GPS Pathfinder XB receiver, or a GPS Pathfinder XC receiver, or the Trimble Yuma rugged tablet computer, Trimble recommends that you set the minimum SNR to 12 dBHz.
![]() The Minimum SNR Mask only applies to L1 data. If a satellite is outputting L1 and L2 signals, and the SNR of the satellite’s L1 signal meets the required minimum SNR, then the L2 signal from the same satellite is always used.
The Minimum SNR Mask only applies to L1 data. If a satellite is outputting L1 and L2 signals, and the SNR of the satellite’s L1 signal meets the required minimum SNR, then the L2 signal from the same satellite is always used.
Min. Satellites: Default: 4 (for three-dimensional positions). Use this property to view and set the minimum number of GPS satellites that must be tracked by the Trimble GPS receiver before a GPS position is calculated. If the receiver detects a lower number of satellites in the sky, it stops calculating positions until the number of qualified satellites (that meet the other property requirements) meets or exceeds the value of this property.
The minimum number of satellites required to calculate a three-dimensional position is four, which is the default setting. If you want to collect high-accuracy data, the minimum number of satellites required to calculate a three-dimensional position when the GPS receiver is moving is five (for example, when logging an area or line feature).
Apply Velocity Filter: Default: Off. Use this property to enable or disable the position velocity filter in the connected Trimble GPS receiver. Velocity filtering smooths the positions from the GPS receiver as they are generated, using velocity information. This filter reduces the effects of multipath on positions computed by the GPS receiver.
![]() Files collected with the Velocity Filter property enabled cannot be differentially corrected using Trimble postprocessing software unless H-Star data or carrier phase measurements are logged.
Files collected with the Velocity Filter property enabled cannot be differentially corrected using Trimble postprocessing software unless H-Star data or carrier phase measurements are logged.
Velocity filtering is not appropriate in all environments, and should only be applied in situations where hostile GPS conditions are expected to degrade position accuracy. When used on predominantly good data, the filtering may decrease the accuracy of the data. Trimble recommends that you apply velocity filtering during differential correction. This gives you the flexibility to reprocess the data with and without velocity filtering, and then choose the best result.
![]() When using a Juno SB, Juno SC, or Juno ST handheld, a GPS Pathfinder XB receiver, or a GPS Pathfinder XC receiver, or the Trimble Yuma rugged tablet computer, velocity filtering is unavailable.
When using a Juno SB, Juno SC, or Juno ST handheld, a GPS Pathfinder XB receiver, or a GPS Pathfinder XC receiver, or the Trimble Yuma rugged tablet computer, velocity filtering is unavailable.
Use GLONASS (if available): Default: On. Use this property to enable or disable tracking of GLONASS satellites in the connected GPS receiver. If the connected receiver is not GLONASS-capable, the setting for this property has no effect and only GPS satellites are tracked.
Tracking GLONASS satellites as well as GPS satellites can improve productivity by reducing the time required to achieve real-time or postprocessed decimeter or subfoot solutions and increasing the amount of data collected (increased yield), particularly in tough environments such as around tall buildings and under heavy tree canopy.
Trimble GPS Settings panel - Real-time tab
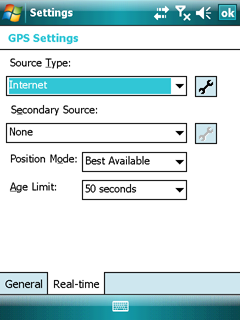
Real-time Settings
Use the Real-time Settings form to select the real-time differential GPS sources that you use, if any, and to configure how your system communicates with each source.
Note – Data collected using a Recon GPS CF Card receiver cannot be differentially corrected, either in real time or using postprocessing.
To open the Real-time Settings tab, do one of the following:
●In the GPS Settings panel, tap Real-time.
●In any screen in the Real-time section, tap the Setup button. ![]()
DigiTerra Explorer always uses the highest priority real-time source available, according to your list of preferences. If the source it is currently using becomes unavailable, the software switches to the next choice. Whenever DigiTerra Explorer acquires a higher priority real-time source, it switches back to this source. For example, the software will not use your second choice if your first choice is available.
It is important that you set up all of the choices correctly, so that when DigiTerra Explroer software switches between choices it can continue to receive corrections.
Source types
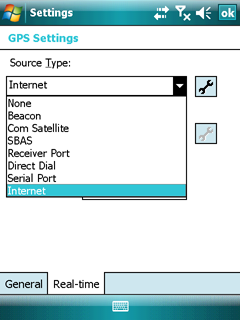
Selectable source types
Default: None to both Source Types
None: The application will not use a real-time DGPS correction stream
Beacon: The application will use real-time DGPS corrections from a marine radio beacon, received by the GPS receiver's integrated beacon receiver
Com Satellite: The application will use real-time DGPS corrections from a satellite differential correction service, received by the GPS receiver's integrated communication satellite receiver
SBAS: The application will use real-time DGPS corrections from a Satellite Based Augmentation System (SBAS), received by the GPS receiver's integrated SBAS receiver
Receiver Port: The application will use real-time DGPS corrections from an external real-time correction source connected to a port on the GPS receiver
Direct Dial: The application will use real-time DGPS corrections from an external real-time correction source connected to the field computer using a direct dial modem
Serial Port: The application will use real-time DGPS corrections from an external real-time correction source connected to a serial port on the field computer
Internet: The application will use real-time DGPS corrections from an external real-time correction source connected to the field computer using an Internet connection